Seamless Connections: The Magic of Laser Welding Machines
In the realm of manufacturing and industrial processes, the art of welding plays a crucial role in joining materials to create strong and durable structures. Among the various welding techniques available, laser welding has emerged as a powerful and versatile method that offers precision, efficiency, and quality in creating seamless connections. The magic of laser welding machines lies in their ability to fuse materials with unparalleled accuracy and speed, revolutionizing industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to electronics and medical devices. Let’s delve into the world of laser welding machines, exploring their capabilities, applications, and the transformative impact they have on modern manufacturing processes.
The Technology Behind Laser Welding Machines
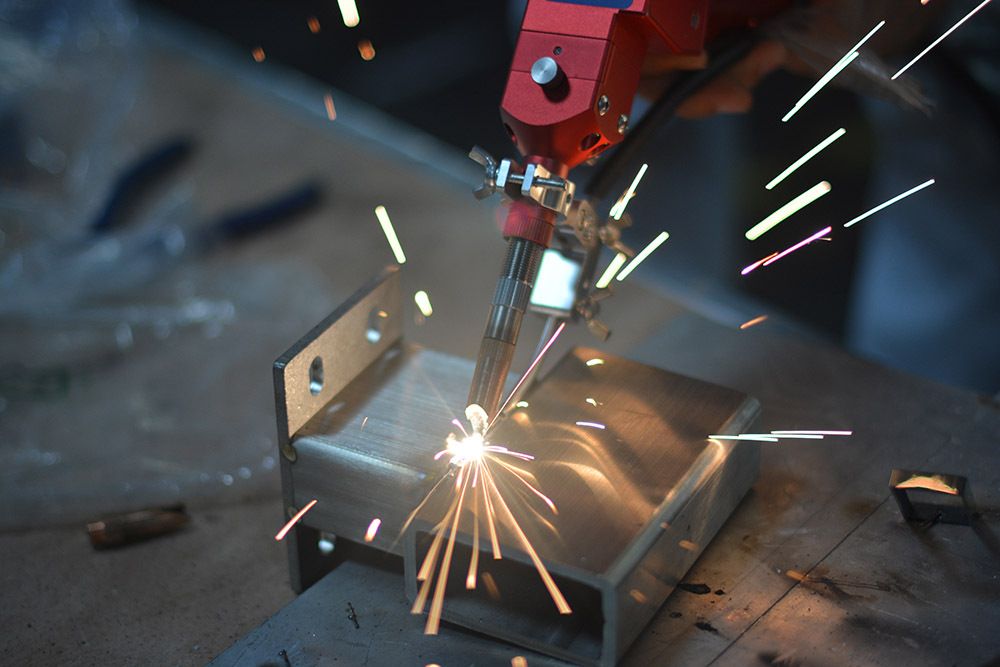
At the heart of laser welding machines is the use of high-powered laser beams to melt and fuse materials together. These machines utilize focused laser energy to create a localized heat source that rapidly melts the workpieces, allowing for precise and controlled welding. The key components of a laser welding system include the laser source, optics for beam delivery and focusing, a workpiece handling system, and control software to manage the welding process.
Laser welding can be performed using different types of lasers, such as fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, and solid-state lasers, each offering unique advantages in terms of power, wavelength, and beam quality. Fiber lasers, in particular, have gained popularity for their high energy efficiency, compact size, and ability to deliver intense laser beams ideal for welding a wide range of materials.OMTech is one of the best brands for laser welding machines.
Advantages of Laser Welding Machines
Precision and Accuracy: Laser welding machines offer exceptional precision, allowing for narrow weld seams and intricate welding patterns with minimal heat-affected zones. This level of accuracy is crucial for applications where tight tolerances and high-quality welds are required.
Speed and Efficiency: Laser welding is a fast and efficient process, enabling rapid welding speeds and high throughput in manufacturing operations. The focused laser beam can quickly melt and solidify the materials, resulting in shorter processing times and increased productivity.
Versatility: Laser welding machines are versatile tools that can weld a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of industries, from automotive and aerospace to electronics and jewelry manufacturing.
Non-Contact Welding: Unlike traditional welding methods that require physical contact between the welding tool and the workpiece, laser welding is a non-contact process. This minimizes the risk of contamination, distortion, and damage to delicate materials, making it ideal for precision welding applications.
Quality and Consistency: Laser welding produces high-quality welds with excellent mechanical properties and aesthetic appeal. The controlled heat input and precise energy delivery result in strong, uniform welds that meet stringent quality standards.
Applications of Laser Welding Machines
Automotive Industry: Laser welding machines are widely used in the automotive industry for joining components such as body panels, exhaust systems, and fuel tanks. The precise and high-speed welding capabilities of laser machines ensure strong and durable welds in automotive assemblies.
Aerospace and Defense: In the aerospace and defense sectors, laser welding is employed for fabricating critical components like aircraft structures, engine parts, and missile components. The ability of laser welding machines to produce lightweight and high-strength welds is essential for aerospace applications.
Electronics Manufacturing: Laser welding plays a vital role in the production of electronic devices, where miniature and intricate welds are required. Printed circuit boards, sensors, and microelectronic components are often assembled using laser welding machines for precise and reliable connections.
Medical Device Manufacturing: The medical device industry relies on laser welding for creating hermetic seals in implants, surgical instruments, and medical equipment. The clean and precise welds produced by laser machines ensure the integrity and safety of medical devices used in healthcare settings.
Jewelry and Watchmaking: Laser welding machines are valued in the jewelry and watchmaking industries for their ability to create fine and detailed welds on precious metals and alloys. Jewelers use laser welding for repairing delicate jewelry pieces and crafting intricate designs with precision.
Challenges and Future Developments
While laser welding machines offer numerous advantages, they also present challenges such as high initial costs, maintenance requirements, and the need for skilled operators. Addressing these challenges through advancements in laser technology, automation, and training programs will be crucial for expanding the adoption of laser welding in various industries.
The future of laser welding machines holds exciting possibilities, with ongoing research and development focused on enhancing process efficiency, expanding material compatibility, and integrating advanced monitoring and control systems. Innovations such as hybrid laser welding, remote laser welding, and additive manufacturing with lasers are reshaping the landscape of welding technology, opening new avenues for creating complex and innovative structures with precision and speed.
Conclusion
In the world of manufacturing, where precision, speed, and quality are paramount, laser welding machines stand out as transformative tools that enable seamless connections and durable welds across a wide range of materials and industries. The magic of laser welding lies in its ability to merge cutting-edge technology with precision engineering, offering a versatile and efficient welding solution that drives innovation and excellence in modern manufacturing processes. As laser welding continues to evolve and advance, its impact on industries worldwide will be felt in the form of stronger, lighter, and more intricately crafted products that shape the future of manufacturing and engineering.












Post Comment